
Изображения могут отличаться от продукта. Подробнее см. технические характеристики.
Поиск нужной модель подшипника.
Стандарт
GB,ASTM/AISI,ГОСТ,BS,JIS,NF,DIN / VDEh
Материал
GCr15
Бренд
QIBR/OEM/Neutral
Применения
Automotive Industry, Aerospace Industry, Industrial Machinery, Construction and Agricultural Equipment, Household Appliances, Marine Industry, Medical Equipment, etc
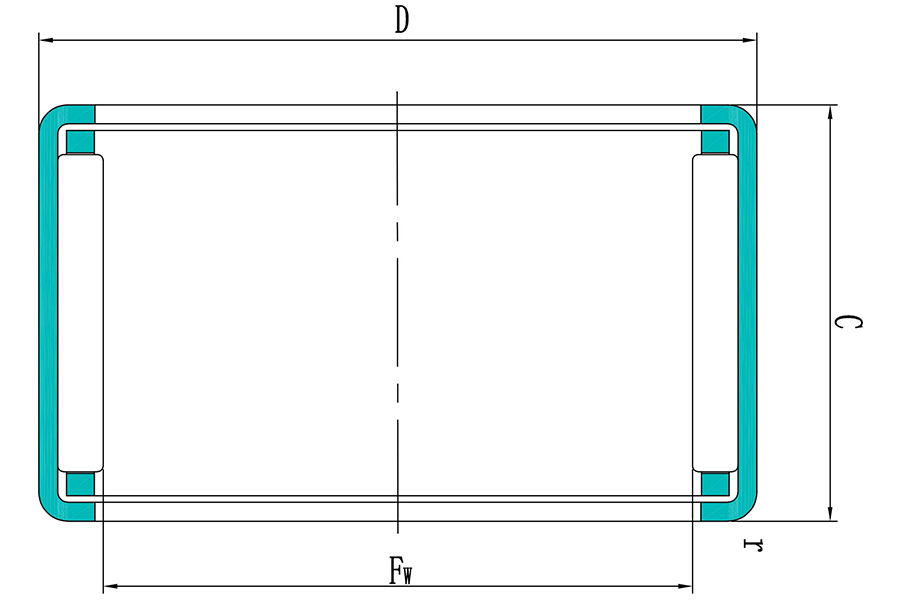
| NO. | Product | Product Number | Базовая динамическая нагрузка | Базовая статическая нагрузка | Диаметр под роликами (Fw) | Предел усталостной нагрузки (Pu) | Вес |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |

|
HK 0306 TN | 1.23 KN | 0.88 KN | 3 mm | 0.088 KN | 1 g |
| 2 |

|
HK 0408 | 1.76 KN | 1.37 KN | 4 mm | 0.14 KN | 2 g |
| 3 |

|
HK 0509 | 2.38 KN | 2.08 KN | 5 mm | 0.22 KN | 2 g |
| 4 |

|
HK 0608 | 2.01 KN | 1.73 KN | 6 mm | 0.18 KN | 2.1 g |
| 5 |

|
HK 0609 | 2.81 KN | 2.7 KN | 6 mm | 0.285 KN | 2.5 g |
| 6 |

|
HK 0709 | 3.03 KN | 3.05 KN | 7 mm | 0.325 KN | 2.6 g |
| 7 |

|
HK 0808 | 2.7 KN | 2.75 KN | 8 mm | 0.285 KN | 2.7 g |
| 8 |

|
HK 0810 | 3.69 KN | 4.05 KN | 8 mm | 0.44 KN | 3 g |
| 9 |

|
HK 0812.2RS | 2.7 KN | 2.75 KN | 8 mm | 0.285 KN | 3.3 g |
| 10 |

|
HK 0908 | 3.52 KN | 3.9 KN | 9 mm | 0.415 KN | 3 g |
| 11 |

|
HK 0910 | 4.13 KN | 4.8 KN | 9 mm | 0.53 KN | 4 g |
| 12 |

|
HK 0912 | 5.12 KN | 6.4 KN | 9 mm | 0.72 KN | 4.6 g |
| 13 |

|
HK 1010 | 4.29 KN | 5.3 KN | 10 mm | 0.57 KN | 4.1 g |
| 14 |

|
HK 1012 | 5.39 KN | 6.95 KN | 10 mm | 0.78 KN | 4.8 g |
| 15 |

|
HK 1014.2RS | 4.29 KN | 5.3 KN | 10 mm | 0.57 KN | 4.6 g |
| 16 |

|
HK 1015 | 6.6 KN | 9 KN | 10 mm | 1.02 KN | 6 g |
| 17 |

|
HK 1210 | 4.84 KN | 6.4 KN | 12 mm | 0.71 KN | 4.6 g |
| 18 |

|
HK 1212 | 6.27 KN | 7.35 KN | 12 mm | 0.85 KN | 9.5 g |
| 19 |

|
HK 1216.2RS | 6.27 KN | 7.35 KN | 12 mm | 0.85 KN | 11 g |
| 20 |

|
HK 1312 | 6.6 KN | 8 KN | 13 mm | 0.915 KN | 10.5 g |
| 21 |

|
HK 1412 | 6.82 KN | 8.65 KN | 14 mm | 0.98 KN | 10.5 g |
| 22 |

|
HK 1512 | 7.65 KN | 9.5 KN | 15 mm | 1.08 KN | 11 g |
| 23 |

|
HK 1516 | 10.1 KN | 14.6 KN | 15 mm | 1.7 KN | 15 g |
| 24 |

|
HK 1522 | 13 KN | 20 KN | 15 mm | 2.28 KN | 20 g |
| 25 |

|
HK 1612 | 7.37 KN | 9.8 KN | 16 mm | 1.12 KN | 12 g |
| 26 |

|
HK 1616 | 10.5 KN | 15.6 KN | 16 mm | 1.8 KN | 16 g |
| 27 |

|
HK 1620.2RS | 10.5 KN | 15.6 KN | 16 mm | 1.8 KN | 18 g |
| 28 |

|
HK 1622 | 12.8 KN | 19.6 KN | 16 mm | 2.24 KN | 24 g |
| 30 |

|
HK 1712 | 7.65 KN | 10.6 KN | 17 mm | 1.2 KN | 13 g |
| 31 |

|
HK 1812 | 7.92 KN | 11.2 KN | 18 mm | 1.27 KN | 13 g |
| 36 |

|
HK 1816.2RS | 7.92 KN | 11.2 KN | 18 mm | 1.27 KN | 15 g |
| 37 |

|
HK 1816 | 11.2 KN | 17.6 KN | 18 mm | 2.04 KN | 18 g |
| 38 |

|
HK 2010 | 6.16 KN | 8.5 KN | 20 mm | 0.93 KN | 12g |
| 39 |

|
HK 2012 | 8.42 KN | 12.5 KN | 20 mm | 1.4 KN | 14 g |
| 39 |

|
HK 2016 | 12.3 KN | 20.4 KN | 20 mm | 2.36 KN | 19 g |
| 39 |

|
HK 2016.2RS | 8.42 KN | 12.5 KN | 20 mm | 1.4 KN | 18 g |
| 40 |

|
HK 2020.2RS | 12.3 KN | 20.4 KN | 20 mm | 2.36 KN | 23 g |
| 41 |

|
HK 2020 | 15.1 KN | 26.5 KN | 20 mm | 3.15 KN | 24 g |
| 42 |

|
HK 2030 | 20.9 KN | 40.5 KN | 20 mm | 4.75 KN | 35 g |
| 43 |

|
HK 2210 | 7.21 KN | 10.6 KN | 22 mm | 1.2 KN | 13 g |
| 44 |

|
HK 2212 | 8.8 KN | 13.7 KN | 22 mm | 1.56 KN | 15 g |
| 45 |

|
HK 2216.2RS | 8.8 KN | 13.7 KN | 22 mm | 1.56 KN | 18 g |
| 46 |

|
HK 2216 | 13 KN | 22.4 KN | 22 mm | 2.6 KN | 21 g |
| 47 |

|
HK 2220.2RS | 13 KN | 22.4 KN | 22 mm | 2.6 KN | 23 g |
| 48 |

|
HK 2220 | 15.7 KN | 29 KN | 22 mm | 3.45 KN | 26 g |
| 49 |

|
HK 2512 | 10.5 KN | 15.3 KN | 25 mm | 1.76 KN | 20 g |
| 50 |

|
HK 2516.2RS | 10.5 KN | 15.3 KN | 25 mm | 1.76 KN | 27 g |
| 51 |

|
HK 2516 | 15.1 KN | 24 KN | 25 mm | 2.85 KN | 25 g |
| 52 |

|
HK 2530.2RS | 24.2 KN | 45 KN | 25 mm | 5.5 KN | 47 g |
| 52 |

|
HK 2520.2RS | 15.1 KN | 24 KN | 25 mm | 2.85 KN | 31 g |
| 53 |

|
HK 2520 | 19 KN | 32.5 KN | 25 mm | 4 KN | 33 g |
| 55 |

|
HK 2526 | 24.2 KN | 45 KN | 25 mm | 5.5 KN | 44 g |
| 57 |

|
HK 2538 | 33 KN | 65.5 KN | 25 mm | 8 KN | 64 g |
| 58 |

|
HK 2816 | 15.7 KN | 26.5 KN | 28 mm | 3.15 KN | 26.5 g |
| 59 |

|
HK 2820.2RS | 15.7 KN | 26.5 KN | 28 mm | 3.15 KN | 34 g |
| 60 |

|
HK 2820 | 20.1 KN | 36.5 KN | 28 mm | 4.4 KN | 36 g |
| 61 |

|
HK 3012 | 11.7 KN | 18.3 KN | 30 mm | 2.12 KN | 23 g |
| 62 |

|
HK 3016.2RS | 11.7 KN | 18.3 KN | 30 mm | 2.12 KN | 31 g |
| 63 |

|
HK 3016 | 16.5 KN | 29 KN | 30 mm | 3.4 KN | 31 g |
| 64 |

|
HK 3020 | 20.9 KN | 40 KN | 30 mm | 4.75 KN | 38 g |
| 65 |

|
HK 3026 | 27 KN | 54 KN | 30 mm | 6.55 KN | 51 g |
| 66 |

|
HK 3038 | 35.8 KN | 80 KN | 30 mm | 9.5 KN | 76 g |
| 67 |

|
HK 3512 | 12.5 KN | 21.6 KN | 35 mm | 2.45 KN | 27 g |
| 68 |

|
HK 3516 | 17.9 KN | 34 KN | 35 mm | 4 KN | 36 g |
| 68 |

|
HK 3520.2RS | 17.9 KN | 34 KN | 35 mm | 4 KN | 41 g |
| 70 |

|
HK 3520 | 22.9 KN | 46.5 KN | 35 mm | 5.6 KN | 44 g |
| 71 |

|
HK 4012 | 13.4 KN | 24.5 KN | 40 mm | 2.8 KN | 30 g |
| 71 |

|
HK 4016.2RS | 14.5 KN | 27.5 KN | 40 mm | 3.15 KN | 37 g |
| 72 |

|
HK 4016 | 19 KN | 39 KN | 40 mm | 4.55 KN | 39 g |
| 73 |

|
HK 4020.2RS | 19 KN | 39 KN | 40 mm | 4.55 KN | 48 g |
| 74 |

|
HK 4020 | 24.2 KN | 53 KN | 40 mm | 6.4 KN | 54 g |
| 75 |

|
HK 4512 | 14.2 KN | 27.5 KN | 45 mm | 3.2 KN | 33 g |
| 76 |

|
HK 4516 | 20.5 KN | 43 KN | 45 mm | 5.1 KN | 47 g |
| 77 |

|
HK 4520.2RS | 20.5 KN | 43 KN | 45 mm | 5.1 KN | 54 g |
| 78 |

|
HK 4520 | 26 KN | 60 KN | 45 mm | 7.2 KN | 56 g |
| 79 |

|
HK 5020 | 29.2 KN | 63 KN | 50 mm | 7.8 KN | 70 g |
| 80 |

|
HK 5024.2RS | 29.2 KN | 63 KN | 50 mm | 7.8 KN | 81 g |
| 81 |

|
HK 5025 | 36.9 KN | 85 KN | 50 mm | 10.6 KN | 85 g |
| 82 |

|
HK 5520 | 30.3 KN | 67 KN | 55 mm | 8.3 KN | 74 g |
| 83 |

|
HK 5528 | 41.8 KN | 104 KN | 55 mm | 12.9 KN | 105 g |
| 84 |

|
HK 6012 | 17.6 KN | 32 KN | 60 mm | 3.8 KN | 49 g |
| 85 |

|
HK 6020 | 31.9 KN | 75 KN | 60 mm | 9.3 KN | 81 g |
| 86 |

|
HK 6032 | 51.2 KN | 137 KN | 60 mm | 17 KN | 136 g |
Особенности и преимущества игольчатых роликовых подшипников с вытянутой чашкой QIBR
Игольчатые роликовые подшипники с вытянутой чашкой QIBR решают ряд важнейших задач в различных областях, в основном в следующих:
1. Компактная конструкция
Использование игольчатых роликов в качестве тел качения позволяет этим подшипникам воспринимать большие радиальные нагрузки при относительно небольших размерах, что делает их пригодными для установки в ограниченном пространстве, особенно в компактных механических конструкциях.
2. Низкое трение и высокая эффективность
Благодаря точной конструкции между игольчатыми роликами и сепаратором, эти подшипники имеют низкие потери на трение, что снижает тепловыделение и повышает эффективность работы. Это делает их пригодными для использования в высокоскоростных и высокопроизводительных средах.
3. Высокая долговечность
Сепаратор стабилизирует положение игольчатых роликов, уменьшая контакт и износ между ними, тем самым продлевая срок службы подшипника. Правильный зазор и прецизионная конструкция обеспечивают стабильность и надежность в процессе эксплуатации.
4. Низкий уровень шума и вибрации
Рациональная структура между игольчатыми роликами и сепаратором минимизирует контакт между роликами, снижая шум и вибрацию, что делает подшипник идеальным для сред, требующих низкого уровня шума.
5. Адаптация к высокоскоростным приложениям
Благодаря малой форме игольчатых роликов и уменьшенной площади контакта, эти подшипники хорошо подходят для высокоскоростных применений, эффективно предотвращая чрезмерное трение и перегрев на высоких скоростях.
Повышение производительности и решения для игольчатых роликовых подшипников с вытянутым стаканом QIBR
1. Улучшенные материалы
Выбор материала с высокими эксплуатационными характеристиками: Использование материалов с повышенной твердостью, износостойкостью и коррозионной стойкостью может значительно повысить долговечность и стабильность подшипника.
2. Оптимизированная конструкция сепаратора
Оптимизация конструкции: Улучшение структуры сепаратора для достижения лучшего расположения игольчатых роликов и равномерного распределения нагрузки. Оптимизация сепаратора уменьшает столкновения игольчатых роликов, повышая стабильность и эффективность работы.
Уменьшение площади контакта: Усовершенствование геометрии сепаратора и расположения игольчатых роликов позволяет минимизировать площадь контакта между роликами, снижая трение и износ.
3. Улучшенные характеристики смазки
Эффективные смазочные материалы: Использование консистентных смазок или масел, подходящих для работы в условиях высоких температур и высокого давления, обеспечивает стабильную работу смазочного материала при длительной эксплуатации, снижая трение и повышая долговечность.
4. Повышенная точность
Прецизионная обработка: Повышение точности изготовления сводит к минимуму погрешности между компонентами подшипника, обеспечивая более равномерный и стабильный контакт между игольчатыми роликами и сепаратором. Это улучшает эксплуатационные характеристики, продлевает срок службы, снижает уровень шума и вибрации.
Основные области применения игольчатых роликовых подшипников с вытянутой чашкой QIBR
1. Сельскохозяйственная техника
Сельскохозяйственное оборудование: В тяжелой сельскохозяйственной технике, такой как тракторы, почвообрабатывающие машины и комбайны, игольчатые подшипники с вытянутым стаканом обеспечивают высокую грузоподъемность при минимальной занимаемой площади, что делает их подходящими для компактных механических конструкций.
2. Промышленное оборудование
Редукторы и трансмиссионные системы: Широко используемые в редукторах и системах с зубчатым приводом, эти подшипники способны выдерживать большие радиальные нагрузки, уменьшать занимаемое пространство и повышать эффективность передачи.
Оборудование для автоматизации: В автоматизированных производственных линиях игольчатые подшипники с вытянутым стаканом поддерживают вращающиеся компоненты, обеспечивая точность и стабильность оборудования.
3. Авиационные двигатели
Турбинные валы и вращающиеся компоненты: В авиационных двигателях игольчатые подшипники с вытянутыми чашками используются в турбовалах, турбинах и других вращающихся компонентах для обеспечения плавной работы на высоких скоростях при восприятии радиальных нагрузок, возникающих при высокоскоростном вращении.
4. Бытовая техника
Бытовая техника: Игольчатые подшипники с вытянутыми чашками широко используются в таких изделиях, как стиральные машины, электрические вентиляторы, электроинструменты и двигатели, обеспечивая высокую эффективность и стабильность при уменьшении занимаемого пространства.


