
Изображения могут отличаться от продукта. Подробнее см. технические характеристики.
Поиск нужной модель подшипника.
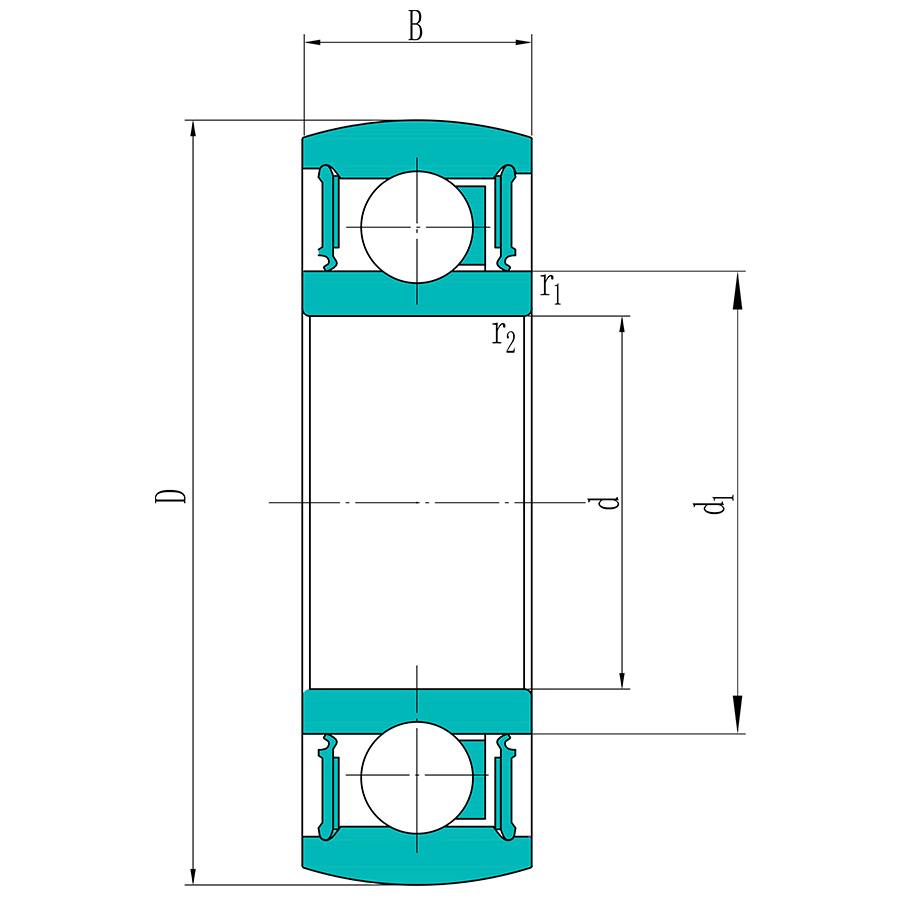
Стандарт
GB,ASTM/AISI,ГОСТ,BS,JIS,NF,DIN / VDEh
Материал
52100, 100Cr6, SUJ2, stainless steel
Внутренний диаметр
17mm-60mm
Наружный диаметр
40mm-110mm
Вес
0.06kg-0.77kg
Бренд
QIBR/OEM/Neutral
Упаковка
QIBR/Standard Industrial Package/OEM
Применения
Conveyor systems, agricultural machinery, food processing equipment, textile machinery, ect
| NO. | Product | Product Number | Базовая динамическая нагрузка | Базовая статическая нагрузка | Отверстие | Вес | Наружный диаметр (D) | Внутреннее кольцо по ширине (B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |

|
1726203-2RS1 | 9.56 KN | 4.75 KN | 17 mm | 0.06 kg | 40 mm | 12 mm |
| 2 |

|
1726204-2RS1 | 12.7 KN | 6.55 KN | 20 mm | 0.1 kg | 47 mm | 14 mm |
| 3 |

|
1726205-2RS1 | 14 KN | 7.8 KN | 25 mm | 0.12 kg | 52 mm | 15 mm |
| 4 |

|
1726305-2RS1 | 22.5 KN | 11.6 KN | 25 mm | 0.22 kg | 62 mm | 17 mm |
| 5 |

|
1726206-2RS1 | 19.5 KN | 11.2 KN | 30 mm | 0.19 kg | 62 mm | 16 mm |
| 6 |

|
1726306-2RS1 | 28.1 KN | 16 KN | 30 mm | 0.34 kg | 72 mm | 19 mm |
| 7 |

|
1726207-2RS1 | 25.5 KN | 15.3 KN | 35 mm | 0.28 kg | 72 mm | 17 mm |
| 8 |

|
1726307-2RS1 | 33.2 KN | 19 KN | 35 mm | 0.44 kg | 80 mm | 21 mm |
| 9 |

|
1726208-2RS1 | 30.7 KN | 19 KN | 40 mm | 0.35 kg | 80 mm | 18 mm |
| 10 |

|
1726308-2RS1 | 41 KN | 24 KN | 40 mm | 0.61 kg | 90 mm | 23 mm |
| 11 |

|
1726209 B-2RS1/VP274 | 33.2 KN | 21.6 KN | 45 mm | 0.39 kg | 85 mm | 19 mm |
| 12 |

|
1726209-2RS1 | 33.2 KN | 21.6 KN | 45 mm | 0.4 kg | 85 mm | 19 mm |
| 13 |

|
1726309-2RS1 | 52.7 KN | 31.5 KN | 45 mm | 0.8 kg | 100 mm | 25 mm |
| 14 |

|
1726309 B-2RS1/VP274 | 52.7 KN | 31.5 KN | 45 mm | 0.81 kg | 100 mm | 25 mm |
| 15 |

|
1726210-2RS1 | 35.1 KN | 23.2 KN | 50 mm | 0.44 kg | 90 mm | 20 mm |
| 16 |

|
1726310 B-2RS1/VP274 | 61.8 KN | 38 KN | 50 mm | 1 kg | 110 mm | 27 mm |
| 17 |

|
1726310-2RS1 | 61.8 KN | 38 KN | 50 mm | 1.05 kg | 110 mm | 27 mm |
| 18 |

|
1726211-2RS1 | 43.6 KN | 29 KN | 55 mm | 0.6 kg | 100 mm | 21 mm |
| 19 |

|
1726212-2RS1 | 52.7 KN | 36 KN | 60 mm | 0.77 kg | 110 mm | 22 mm |
Особенности и преимущества подшипников для корпуса QIBR со стандартными внутренними кольцами
Подшипники для корпуса QIBR со стандартными внутренними кольцами решают несколько ключевых проблем в различных областях, в частности, в следующих аспектах:
1. Способность к самоустановке
Подшипник для корпуса обладает функцией самоустановки. Он состоит из внутреннего кольца, наружного кольца, тел качения и сепаратора. Сферическая форма наружного кольца позволяет подшипнику выдерживать определенные осевые и радиальные погрешности. Даже если вал не идеально выровнен при установке, подшипник может работать правильно, уменьшая повреждения, вызванные ошибками установки.
2. Высокая грузоподъемность
Подшипники для корпуса обычно выдерживают большие радиальные и определенные осевые нагрузки, что делает их пригодными для использования в тяжелом оборудовании.
3. Долговечность и надежность
Благодаря своим конструктивным особенностям, подшипники скольжения износостойки и ударопрочны, демонстрируя высокую надежность в неблагоприятных условиях работы (например, в пыльной или влажной среде).
4. Широкое применение
Подшипники для корпуса широко используются в различном оборудовании, особенно там, где требуется самоустановка и высокая грузоподъемность.
Улучшение характеристик и решения для подшипников QIBR со стандартными внутренними кольцами
1. Улучшение материалов
Высокопроизводительные материалы: Использование высокопрочных и износостойких материалов, таких как керамика, современные легированные стали и нержавеющая сталь, позволяет значительно повысить долговечность и грузоподъемность подшипников-вкладышей.
Обработка поверхности: Обработка поверхности, такая как науглероживание, азотирование, хромирование и закалка, может повысить износостойкость, коррозионную стойкость и усталостную прочность подшипника.
2. Повышение точности
Высокоточное производство: Передовые технологии обработки, такие как обработка на станках с ЧПУ и прецизионная шлифовка, повышают точность обработки подшипника, что приводит к более плавной работе и снижению шума.
Высокоточная посадка: Повышение точности посадки между внутренним и наружным кольцами вставного подшипника обеспечивает гибкость и стабильность вращения подшипника, снижая трение и износ.
Улучшение характеристик уплотнения
3. Эффективное уплотнение
Более эффективные уплотнительные конструкции, такие как двухкромочные уплотнения или скелетные уплотнения, могут эффективно предотвращать попадание пыли и грязи в подшипник, уменьшая загрязнение и продлевая срок службы.
Уплотнительные материалы: Использование термостойких, износостойких и коррозионностойких уплотнительных материалов обеспечивает надежность подшипника в жестких условиях эксплуатации.
4. Повышение грузоподъемности
Оптимизированная конструкция: Оптимизация геометрии подшипников скольжения, например, увеличение площади контакта и применение более прочной конструкции наружного кольца, повышает их грузоподъемность, увеличивая способность подшипника выдерживать нагрузки.
Основные области применения подшипников для корпуса QIBR со стандартными внутренними кольцами
1. Сельскохозяйственная техника
Подшипники для корпуса широко используются в сельскохозяйственной технике, такой как тракторы, сеялки, комбайны и т.д. Эти машины часто подвергаются высоким нагрузкам и могут испытывать осевое или радиальное смещение, поэтому самоустанавливающиеся свойства подшипников вкладышей очень подходят для таких условий.
2. Строительная техника
Подшипники для корпуса широко используются в строительной технике, такой как краны, экскаваторы и бетономешалки. Строительная техника часто работает в условиях высоких нагрузок и сильных ударов, а высокая грузоподъемность и самоустанавливающиеся свойства подшипников вкладышей помогают оборудованию работать более плавно.
3. Автомобильная промышленность
В автомобильных системах подвески, колесных осях и компонентах рулевого управления широко используются подшипники-вкладыши. подшипники для корпуса способны выдерживать обратные ударные нагрузки и боковые силы от шин и систем подвески, что делает их идеальными для применения в автомобильной промышленности.
4. Конвейерное оборудование
Подшипники-вкладыши широко используются в различном транспортировочном оборудовании, таком как конвейерные ленты, ленточные и роликовые конвейеры. подшипники для корпуса способны адаптироваться к изменениям нагрузки на конвейерное оборудование и осевому смещению, вызванному длительной эксплуатацией оборудования


